How to improve food systems by looking to nature for design solutions – this was the brief given to entrants in the Biomimicry Institute’s Global Design Challenge, which announced its finalists this week. The selection committee has drawn up a list of eight teams, each of which has been invited to prototype its solution in an accelerator program that will award US$100,000 to the winner.
The Biomimicry Institute engaged 60 judges, including biologists, business leaders, venture capitalists, and agriculture experts to examine nearly 2,000 entries from more than 70 countries and select eight finalists. Key food and agriculture issues like waste, packaging, agricultural pest management, food distribution, and energy use were the focus of this year's Challenge.
"Entrepreneurs don’t have the same R&D budgets as big companies, but those who are patient enough to understand and employ nature’s designs have a distinct advantage: they are leveraging millions of years of evolution," says Beth Rattner, executive director of the Biomimicry Institute. "That’s what we’re seeing with these amazing submissions. They aren’t just good ideas; they’re proof points that radically sustainable products are possible."
In no particular order, the final eight projects are:
- Hexagonal shapes in nature was the inspiration for Italy's Team Hexagro, which was shortlisted for its so-called groundless growing system that allows people to grow food in limited spaces. The modular system is made of biodegradable, recycled materials and the team says that one tree could produce 342 lettuce plants from a 2 sq m (21.5 sq ft) plot, compared to 80 sq m in traditional agriculture. It features an automatic irrigation system and a smartphone app is in the works.

- A team from South Africa looked to animal collectives such as a flock of birds or a school of fish for inspiration when designing the Holonic Integrated Produce Swarm app. The peer-to-peer networking app is aimed at small-scale, intensive food production systems and could help create local and regional "swarms" and produce hubs, facilitating distribution and avoiding waste.
- The Team Penthouse Protozoa (Oregon, US) looked to the earthworm’s digestive system and the human small intestine as a biomimetic reference for a drainage system that keeps nutrients in the soil rather than losing them in runoff.

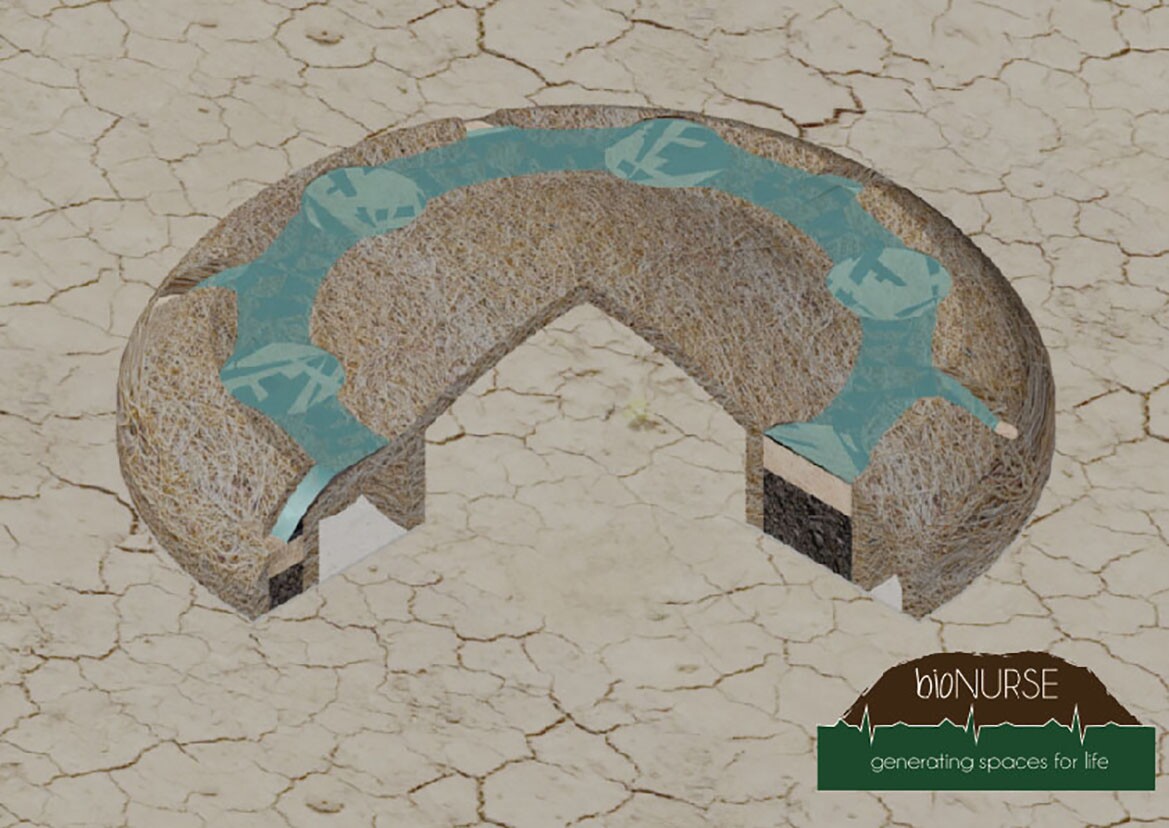
- Noting that hardy nurse plants can help recover degraded soils and set the stage for new plants to grow, Chile's BioNurse aims to restore soil by improving conditions for seedlings and exposing them to a mix of nutrients, microbiology and hygroscopic components.
- From Thailand, the BioX team believes that edible insects are the food of the future and developed an insect-capturing chamber called Jube.

- The Balcony Cultivator from the Technical University in Zvolen, Slovakia, has been designed for spatially-challenged urban farmers. Moisture is reportedly drawn up from the bottom of the device and condenses in a dome to the top, before being channeled to the roots of the resident plants. Inspiration came from lizards living in arid areas that can collect water and moisture with their skin.

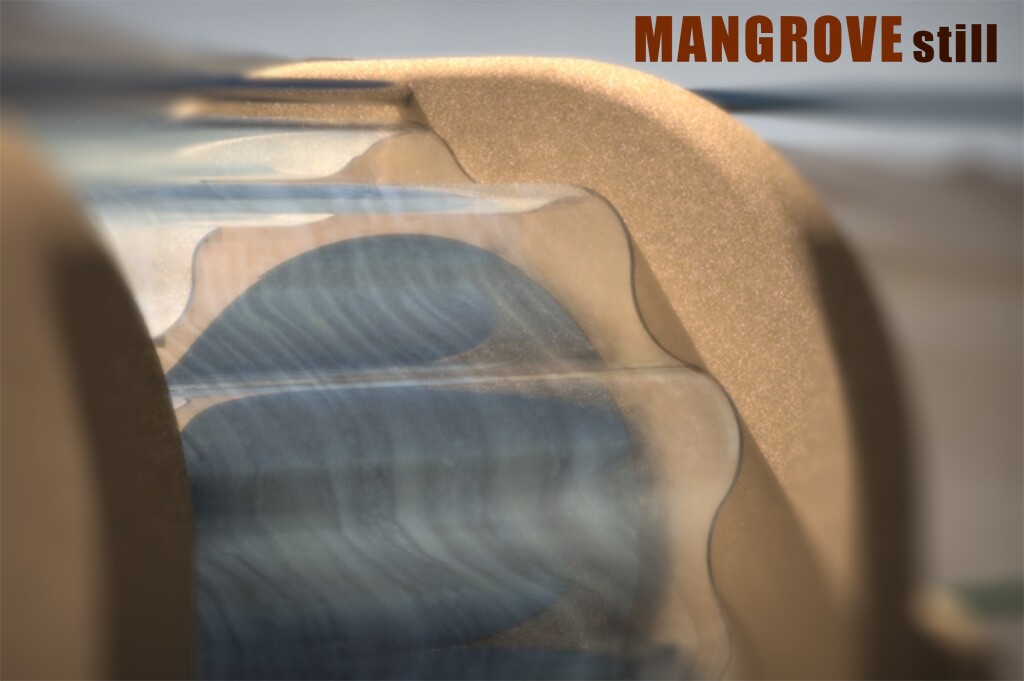
- Team Planet, also from Italy, looked at mangroves and salt marshes to find a solution for land degradation and water scarcity in coastal areas. Its Mangrove Still is a desalinating solar unit that can produce fresh water for irrigation.

- The Oasis Aquaponic Food Production System depends on the symbiotic relationship between plants and fish. The solar-powered farming solution sees fish waste feeding the plants and the plants cleaning the water for the fish.

The finalists will present their projects at SXSW Eco in Austin, Texas (October 5-7), pitching the marketability of their ideas and participating in an awards event. The teams will then spend the next eight months prototyping and testing, before competing for the $100,000 Ray C. Anderson "Ray of Hope" Prize in 2016.
Source: Biomimicry Institute